ACFS and ADVM
System configuration
We will use the system configured and installed in part 2
General information
- ADVM = ASM dynamic volume manager
- ACFS = ASM cluster file system
- Basic layout
(Source: Oracle Database Storage Administrator’s Guide 11g Release 2)
ADVM – Advantages
- Integrated in ASM; this can be an disadvantage as well :-)
- Inhertits storage from ASM hence enables host-based mirroring (either 2- or 3-way-mirroring)
- multiple volumes within a disk group can be created with an file system such as ext3, ext4, reiserfs, … on top of it and will support storage of any file type as the file system normally woud – EXCEPT files which can be place in ASM directly
- ADVM volume dynamically resizeable
ADVM – Disadvantages
- ADVM volumes may be resized online; but the used file system must support it as well (ext3 on OEL 5 does support online resizing but does not support online shrinking)
- Storing files which can be stored in ASM directly in ADVM + file system is not supported
- NFS on top of ADVM is also not supported
- ASM configuration assistant (asmca) only supports creation of volumes / file system… delete a volume / file system requires command line
ACFS – Advantages
- cluster file system on top of ASM and ADVM
- as available as ASM is (inherits storage from ASM disk group and ADVM volume)
- Supports storage of files which cannot be directly stored in ASM, i.e.
- executables
- trace files
- log files
- …
- Supports even oracle database binary installations
- On ACFS read-only Snapshots can be created
- dynamically resizeableUseable accross plattforms
- Thoughts
- Do i need licenses for grid infrastructrue?
- If not: What if grid infrastructure + ASM used to provide host-based mirroring and cluster file system for non-oracle applications, for instance web servers ACFS Mount registry: used for mouting ACFS and ADVM file system across reboots
ACFS – Disadvantages
- for example storing database files in ACFS is not supported, according to the documentation
„Oracle Support Services will not take calls and development will not fix bugs associated with storing unsupported file types in Oracle ACFS“ - Only available with RedHat Server 5 or Oracle Enterprise Linux 5 !
- Disk group compatible parameter COPATBILE.ASM and COMPATIBLE.ADVM must be set so 11.2
- ASM configuration assistant (asmca) only supports creation of volumes / file system… delete a volume / file system requires command line
First steps with ADVM and ACFS
Create a disk group for use with ADVM and ACFS
Lets first create an additional disk group called „DATA2“ which consists for two iSCSI LUNs with 30 GB each
Preparation:
- LUNs visible with „fdisk -l“
- Partition created (one on each LUN)
- disk labeled with „oracleasm createdisk <name> <devpath>“
- Create disk group in ASM (remember to connect as „sys as sysASM“!)
- Notes on disk groups
- AUSIZE of 4 MB recommended by Oracle documentation due to:
- Increased I/O through the I/O subsystem if the I/O size is increased to the AU size.
- Reduced SGA size to manage the extent maps in the database instance.
- Faster datafile initialization if the I/O size is increased to the AU size.
- Increased file size limits.
- Reduced database open time.
- Large AUSIZE requires as well
- Increasing size of maximum IO request to at least 4 MB in operating system, drive, HBA, storage system
- Larger stripe size in storage system (pre 11g R2: 1 MB stripe size, with 11g R2: 4 MB? → to be tested)
- AUSIZE of 4 MB recommended by Oracle documentation due to:
Read the documentation on COMPATIBLE parameters;most „cool“ features are only available with 11.2 COMPATIBLE parameter hence require 11g R2 database
Creating an ADVM and afterwards an ACFS
Create an ADVM
- ACFS requires ADVM in which ACFS can be created
- volcreate creates ADVM volume
- The command above shows minimal command creating an ADVM volume; redundancy is derived from disk group, our data group was created with „normal“ redundancy so the volume inherits this as well)
- Creation with SQL also possible: „ALTER DISKGROUP data2 ADD VOLUME volume1 SIZE 10G;“
Create ACFS on top of ADVM
- Requires ADVM in which ACFS can be created
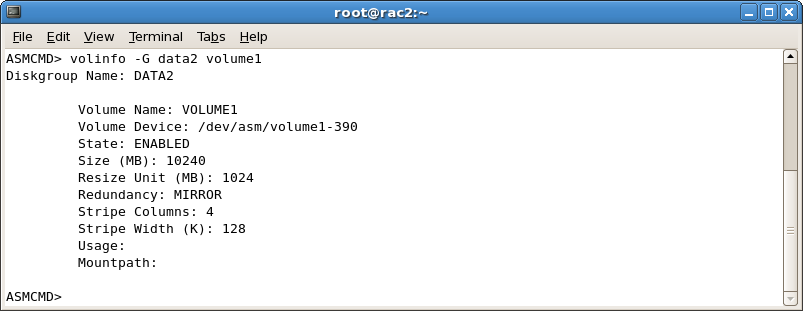
- volinfo shows detailed information
- Especially device path is important for creating the file system
- create ACFS from operating system (only on one node)
- register acfs in registry to be mounted across reboots with „acfsutil“
- ATTENTION: DO NOT register shared oracle home directories with acfsutil; this will be done later by the clusterware itself!
- test of everything works by issueing „mount.acfs -o all“ on all nodes; the file system should be mounted and accessible
Simple Performance tests
dd if=/dev/zero bs=1024k of=<path> count=1000 oflag=direct
→ direct I/O used; no caching, performed 10 times
- write to ACFS
- ACFS 2-way mirror: ~ 6 MB/s average
- ACFS unprotected: ~ 12 MB/s averga
- → expected… one disk, double I/O halfed throughput
- direct write to iSCSI LUN: ~ 14.3 MB/s average
Attention: Tests were performed within a VMWare… so results are most likely not accurate… but we get an impression.. we will check this on real hardware later!






Pingback: Ronny Egners Blog » ACFS Snapshots
how to use GFS with 11gR2?
If supported (you have to check the grid installation guide) i guess basically the same way as ADVM+ACFS….prior grid installation configure GFS and mount home directories. Then install grid infrastructure.
@Ronny Egner
do i need lock server node for this?for using GFS
http://www.redhat.com/docs/manuals/csgfs/oracle-guide/ch-overview.html#S1-OV-SAMPLENET
and
http://www.redhat.com/docs/manuals/csgfs/oracle-guide/s1-gfs-conffiles.html
regards
I dont know. I have not used GFS before. If you want some kind of clustered file system use ACFS or NFS.
@Ronny Egner
do i need lock server to configure GFS?
as i need only share fs so i may not use lock server is nt it?
regards
I dont know. I have never used GFS before.
@Ronny Egner
hi
i really do not want to use iscsi and SAN storage,is it mandatory ?
is there any option to by pass it?
regards
You can basically use NFS. But NFS+ASM dont work that nice together; but you can try it of course.